字典管理
概述
字典管理是系统中用于维护和管理枚举数据的核心功能,通过统一的数据字典机制,实现业务枚举值的集中管理与灵活调用。
核心特性:
- 🚀 智能缓存 - 基于 Pinia 状态管理的缓存机制,首次加载后自动缓存,避免重复请求
- 📦 按需加载 - 仅在需要时从后端获取数据,后续调用直接读取缓存
- ⚡ 性能优化 - 显著减少 HTTP 请求次数,提升页面响应速度
- 🔄 统一管理 - 集中维护枚举数据,修改后即时生效
- 💡 易于使用 - 简洁的 API 设计,支持快速集成到业务代码中
工作原理
采用 Pinia 缓存机制,字典数据在首次请求后会自动缓存到前端状态管理中。后续对相同字典的调用将直接从缓存读取,无需频繁查询后台接口,大幅提升系统性能和用户体验。
详细实现逻辑请参考 前端指南 - 字典数据管理。
核心 API
系统提供两个核心方法用于字典数据的获取和展示:
getDict - 获取字典数据
功能说明: 根据字典名称获取对应的字典数据,支持智能缓存。
配置文件: src/utils/dictionary.js
import { useDictionaryStore } from "@/pinia/modules/dictionary";
/**
* 获取字典数据(支持缓存)
* @param {string} name - 字典名称
* @returns {Promise<Array>} 字典数据数组 [{label: string, value: string}]
*
* @description
* 1. 首次调用:从后端 API 获取数据,并缓存到 Pinia Store
* 2. 后续调用:直接从缓存读取,无需请求后端接口
* 3. 缓存持续时间:整个用户会话期间(刷新页面后重新加载)
*/
export const getDict = async (name) => {
const dictionaryStore = useDictionaryStore();
// getDictionary 方法内部实现了缓存逻辑
await dictionaryStore.getDictionary(name);
return dictionaryStore.dictionaryMap[name];
};缓存机制说明:
graph LR
A[调用 getDict] --> B{缓存中是否存在?}
B -->|是| C[直接返回缓存数据]
B -->|否| D[请求后端 API]
D --> E[缓存到 Pinia Store]
E --> F[返回数据]
C --> G[无 HTTP 请求]
F --> H[后续调用走缓存]性能优势
假设某个字典在页面中被调用 10 次:
- 不使用缓存:发起 10 次 HTTP 请求
- 使用缓存:仅发起 1 次 HTTP 请求,后续 9 次直接读取内存
性能提升:减少 90% 的网络请求 ⚡
showDictLabel - 显示字典标签
功能说明: 根据字典值(code)查找并返回对应的字典标签(label)。
/**
* 显示字典的标签值
* @param {Array} dict - 字典数据数组
* @param {string|number} code - 字典值
* @param {string} keyCode - 字典值字段名,默认 'value'
* @param {string} valueCode - 字典标签字段名,默认 'label'
* @returns {string} 对应的字典标签,未找到返回空字符串
*
* @example
* const dict = [{label: '菜单', value: '1'}, {label: '按钮', value: '2'}]
* showDictLabel(dict, '1') // 返回: '菜单'
* showDictLabel(dict, '3') // 返回: ''
*/
export const showDictLabel = (
dict,
code,
keyCode = "value",
valueCode = "label"
) => {
if (!dict) {
return "";
}
const dictMap = {};
// 构建字典映射表,提高查找效率
dict.forEach((item) => {
if (Reflect.has(item, keyCode) && Reflect.has(item, valueCode)) {
dictMap[item[keyCode]] = item[valueCode];
}
});
return Reflect.has(dictMap, code) ? dictMap[code] : "";
};后台配置指南
1. 创建字典分类
字典名称是字典数据的唯一标识符,用于在代码中引用对应的字典数据。
操作步骤:
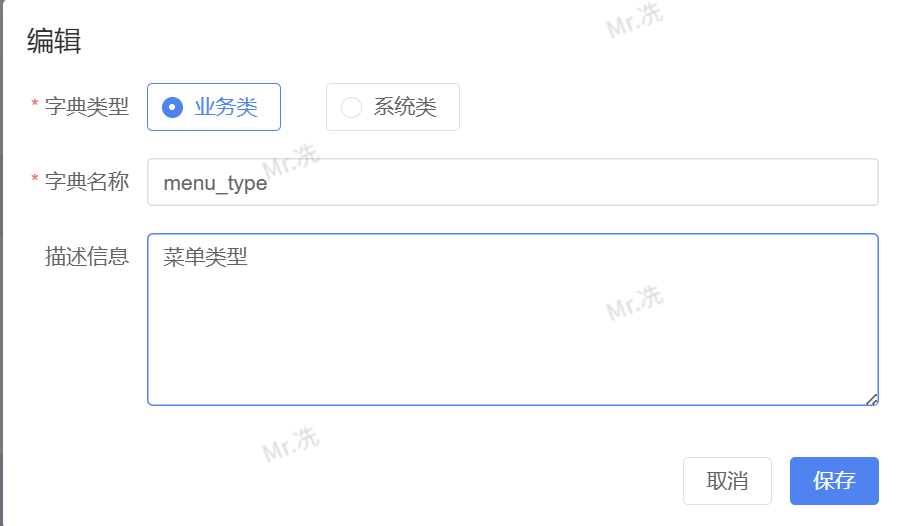
- 进入 系统管理 > 字典管理 界面
- 点击 新增 或选择已有字典点击 编辑
- 在 字典名称 字段中填入字典标识(如:
menu_type、user_status) - 填写 字典描述 等其他必要信息
- 点击 确定 保存
命名规范
- 必须使用英文字符,建议使用小写字母和下划线(如:
menu_type) - 字典名称在系统中必须唯一,不可重复
- 建议采用语义化命名,便于理解和维护(如:
user_status、order_type) - 避免随意修改已有字典名称,可能影响前端代码的正常调用
2. 配置字典明细
字典明细是字典的具体数据项,包含标签(label)和值(value)两个关键字段。
操作步骤:
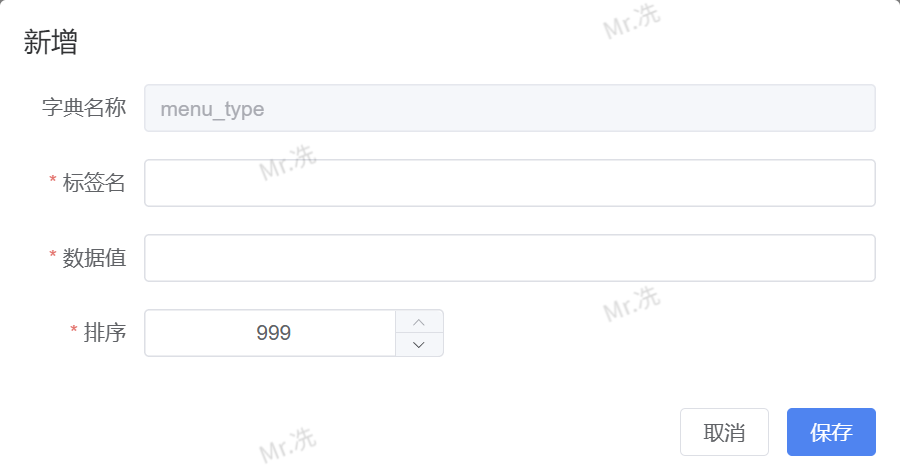
- 进入 系统管理 > 字典管理 界面
- 在左侧列表中点击需要配置的字典名称
- 右侧将显示该字典的明细管理界面
- 点击 新增 按钮,填写以下信息:
- 标签名:用户可见的显示文本(如:
菜单、按钮) - 数据值:程序中使用的值(如:
1、2) - 排序:控制显示顺序
- 备注:字段说明(可选)
- 标签名:用户可见的显示文本(如:
- 点击 确定 保存
最佳实践
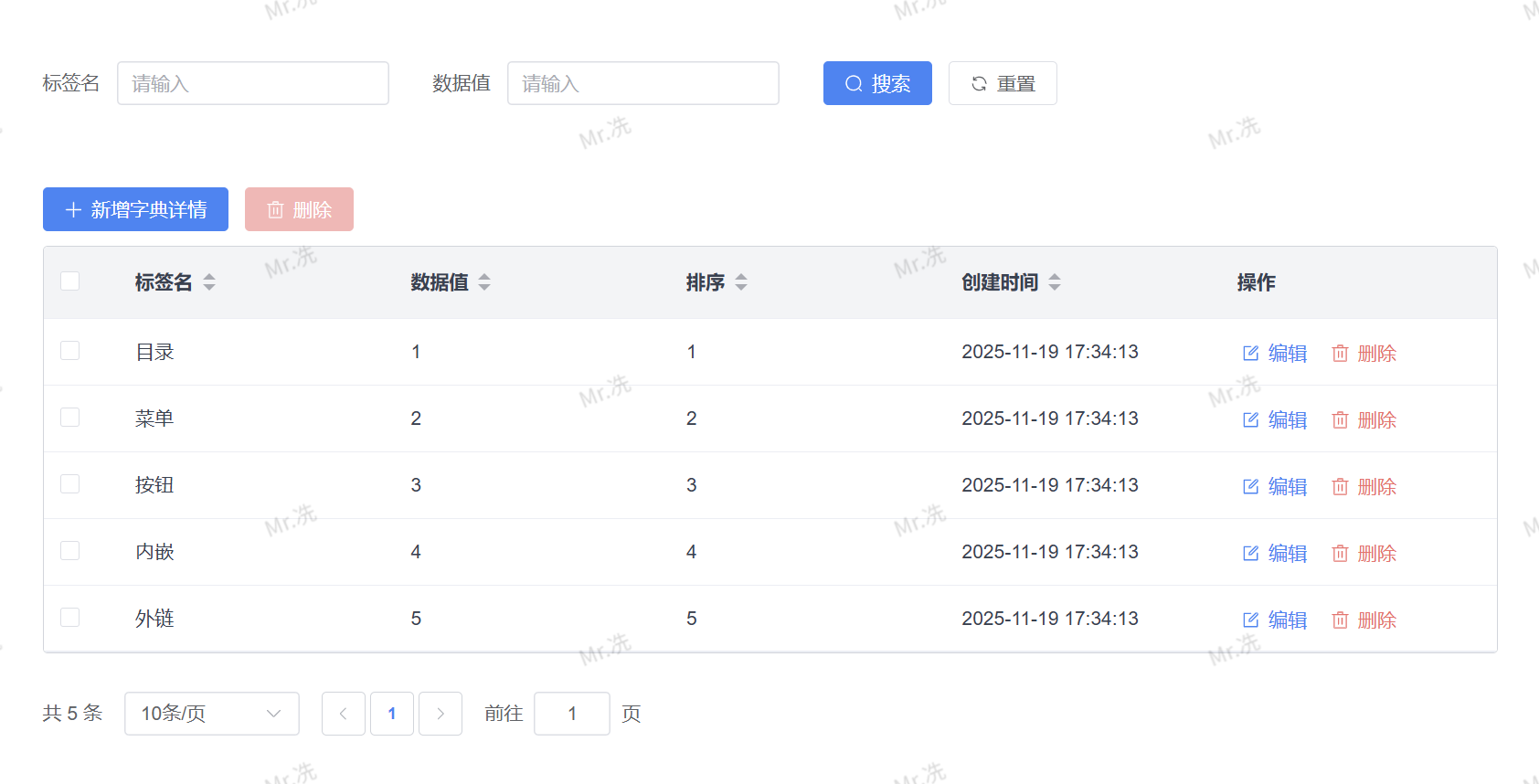
字典数据示例:
| 标签名 | 数据值 | 使用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| 菜单 | 1 | 前端显示"菜单",后端存储"1" |
| 按钮 | 2 | 前端显示"按钮",后端存储"2" |
| 目录 | 0 | 前端显示"目录",后端存储"0" |
优势: 修改标签名时无需修改代码,只需在后台调整即可全局生效。
前端使用实践
步骤 1:获取字典数据
使用 getDict 方法获取字典数据并存储到响应式变量中,该方法会自动利用缓存机制。
示例代码:
<script setup>
import { ref } from "vue";
import { getDict, showDictLabel } from "@/utils/dictionary";
// 定义响应式变量存储字典数据
const menuTypeOption = ref([]);
// 初始化函数 - 加载字典数据
const init = async () => {
// 首次调用:从后端获取并缓存
// 后续调用:直接从 Pinia 缓存读取
menuTypeOption.value = await getDict("menu_type");
};
// 组件挂载时初始化
init();
</script>缓存优势体现
在同一个页面中,如果多个组件都需要 menu_type 字典:
// 组件 A
const menuType1 = await getDict("menu_type"); // 发起 HTTP 请求,缓存数据
// 组件 B
const menuType2 = await getDict("menu_type"); // 直接读取缓存,无 HTTP 请求
// 组件 C
const menuType3 = await getDict("menu_type"); // 直接读取缓存,无 HTTP 请求结果: 3 个组件仅产生 1 次网络请求!
步骤 2:调试验证
在浏览器控制台可以查看字典数据的实际结构,确认数据是否正确加载。
控制台输出示例:
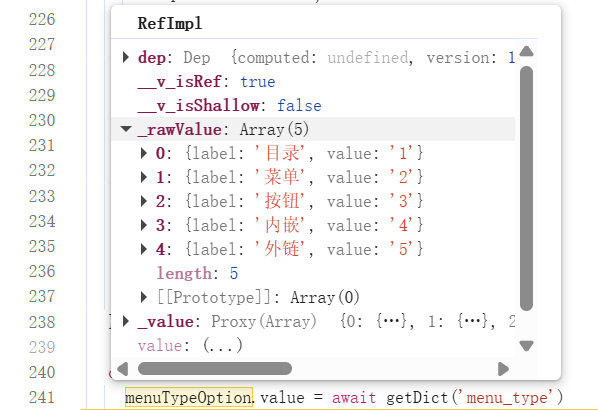
数据结构说明:
[
{ "label": "目录", "value": "0" },
{ "label": "菜单", "value": "1" },
{ "label": "按钮", "value": "2" }
]步骤 3:在表格中显示字典标签
使用 showDictLabel 方法将数据值转换为用户可读的标签文本。
完整示例:
<template>
<el-table :data="tableData">
<!-- 使用 formatter 格式化显示 -->
<el-table-column
align="left"
prop="menuType"
:formatter="
(row, column, cellValue) => showDictLabel(menuTypeOption, cellValue)
"
label="菜单类型"
sortable="custom"
/>
</el-table>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from "vue";
import { getDict, showDictLabel } from "@/utils/dictionary";
const menuTypeOption = ref([]);
const tableData = ref([]);
const init = async () => {
// 加载字典数据
menuTypeOption.value = await getDict("menu_type");
// 加载表格数据
// tableData.value = await fetchTableData()
};
init();
</script>显示效果:
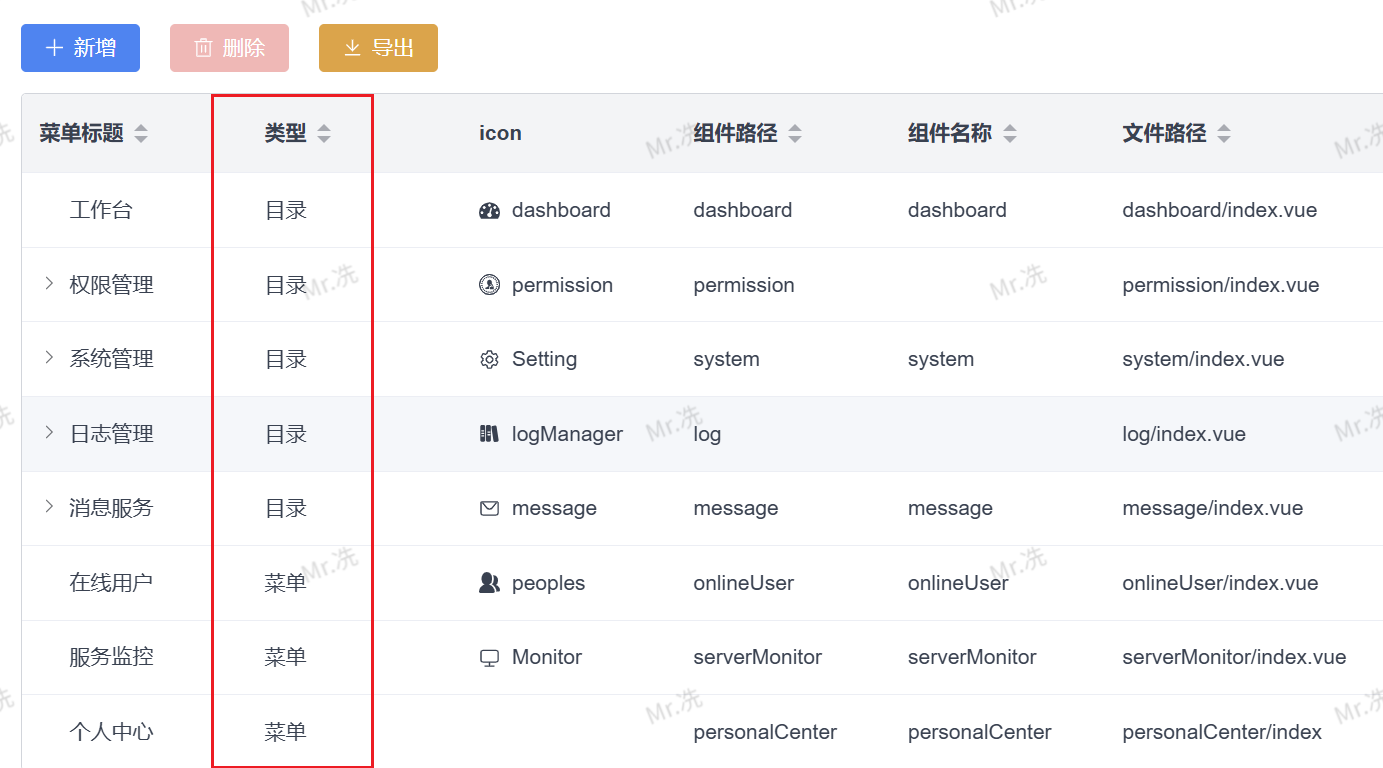
转换对比:
| 后端返回值 | 显示文本 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
"0" | 目录 | 通过 showDictLabel 自动转换 |
"1" | 菜单 | 提升用户体验 |
"2" | 按钮 | 无需硬编码映射关系 |
步骤 4:在下拉选择器中使用
字典数据可以直接用于 Element Plus 的选择器组件。
<template>
<el-form-item label="菜单类型">
<el-select v-model="form.menuType" placeholder="请选择菜单类型">
<el-option
v-for="item in menuTypeOption"
:key="item.value"
:label="item.label"
:value="item.value"
/>
</el-select>
</el-form-item>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, reactive } from "vue";
import { getDict } from "@/utils/dictionary";
const menuTypeOption = ref([]);
const form = reactive({
menuType: "",
});
const init = async () => {
menuTypeOption.value = await getDict("menu_type");
};
init();
</script>常见场景
场景 1:多个字典同时加载
<script setup>
import { ref } from "vue";
import { getDict } from "@/utils/dictionary";
const menuTypeOption = ref([]);
const userStatusOption = ref([]);
const roleTypeOption = ref([]);
const init = async () => {
// 并行加载多个字典(首次调用会请求后端)
const [menuType, userStatus, roleType] = await Promise.all([
getDict("menu_type"),
getDict("user_status"),
getDict("role_type"),
]);
menuTypeOption.value = menuType;
userStatusOption.value = userStatus;
roleTypeOption.value = roleType;
// 后续在其他组件中再次调用这些字典时,将直接从缓存读取
};
init();
</script>场景 2:条件渲染
<template>
<el-tag
v-for="item in menuTypeOption"
:key="item.value"
:type="getTagType(item.value)"
>
{{ item.label }}
</el-tag>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from "vue";
import { getDict } from "@/utils/dictionary";
const menuTypeOption = ref([]);
const getTagType = (value) => {
const typeMap = {
0: "info",
1: "success",
2: "warning",
};
return typeMap[value] || "default";
};
const init = async () => {
menuTypeOption.value = await getDict("menu_type");
};
init();
</script>常见问题
Q1: 如何清除字典缓存?
场景: 后台修改了字典数据,前端需要获取最新数据。
方案 1:刷新页面
// 最简单的方式:刷新页面重新加载所有数据
window.location.reload();方案 2:手动清除缓存
import { useDictionaryStore } from "@/pinia/modules/dictionary";
const dictionaryStore = useDictionaryStore();
// 清除特定字典缓存
delete dictionaryStore.dictionaryMap["menu_type"];
// 重新加载
const newData = await getDict("menu_type");Q2: 字典数据为空怎么办?
可能原因:
- 后台未配置该字典
- 字典名称拼写错误
- 用户无权限访问该字典
调试方法:
const menuType = await getDict("menu_type");
console.log("字典数据:", menuType);
if (!menuType || menuType.length === 0) {
console.error("字典数据加载失败,请检查后台配置");
}Q3: 如何在 JavaScript 代码中使用字典?
import { getDict, showDictLabel } from "@/utils/dictionary";
// 获取字典并使用
const menuType = await getDict("menu_type");
// 方式 1:直接查找
const menuItem = menuType.find((item) => item.value === "1");
console.log(menuItem?.label); // 输出: '菜单'
// 方式 2:使用 showDictLabel
const label = showDictLabel(menuType, "1");
console.log(label); // 输出: '菜单'性能对比
传统方式 vs 缓存机制
传统方式(每次都请求后端):
// ❌ 不推荐:每次调用都发起 HTTP 请求
const getMenuType = async () => {
const response = await fetch("/api/dict/menu_type");
return await response.json();
};
// 10 次调用 = 10 次 HTTP 请求
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
await getMenuType(); // 每次都请求后端
}缓存机制(首次请求,后续读缓存):
// ✅ 推荐:使用 Pinia 缓存
import { getDict } from "@/utils/dictionary";
// 10 次调用 = 1 次 HTTP 请求
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
await getDict("menu_type"); // 首次请求,后续读缓存
}性能提升:
- 网络请求减少:90%+
- 响应时间:从数百毫秒降至 < 1ms
- 用户体验:页面加载更流畅

